Abstract
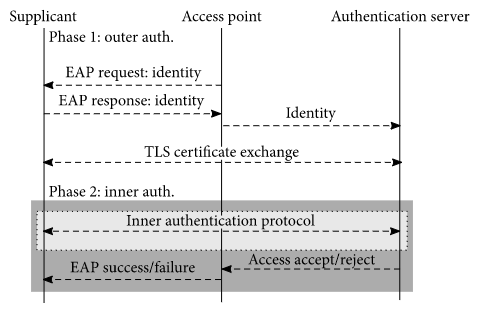
A plethora of organizations, companies, and foremost universities and educational institutions are using WPA2-Enterprise protocol to allow their end-users to connect to provided Wi-Fi networks. When both the provider’s and the end-user’s devices are configured properly, it is considered one of the safest Wi-Fi connection protocols with the added benefits of having a unique password for every Wi-Fi user. However, a known evil twin attack can be performed to steal users’ Wi-Fi login credentials, if the devices are not configured correctly. Considering the widespread use of Wi-Fi-enabled smartphones and rising concerns regarding users’ privacy, we focus on the privacy aspects of WPA2-Enterprise vulnerabilities mainly on the widespread Eduroam network. We show that device deanonymization is a concerning liability of many Eduroam networks. More than 87% of 1650 devices collected during a two-month test on our university are vulnerable to MAC address deanonymization attack. Furthermore, by analyzing the Eduroam Configuration Assistant Tool of 1066 different institutions around the world, 67% of exported Eduroam profiles having the Wi-Fi device reveal the user’s identity in the clear, thus linking the users with the device’s MAC address. Indeed, the analysis of the configuration profiles has been confirmed by performing the deanonymization attack on a large-scale international music festival in our country, where 70% of the devices have been vulnerable. Additionally, we showcase the psychological aspects of secure Eduroam users, where some are willing to modify secure configuration profiles to gain aspects to certain blocked features. As a result, the attacker is granted with user credentials and IMSI number and provided with access to all Eduroam-related services.