- Normalized number of strong attractors in the range domain with
respect to the relative noise level
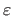 . The results are given for
two values of fixed bandwidth.
. The results are given for
two values of fixed bandwidth.
- Segmentation for different
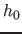 . In images (g) and (h)
segments smaller than 50 pixels are connected to the neighbor with the
most similar color. Region boundaries are superimposed to emphasize
details.
. In images (g) and (h)
segments smaller than 50 pixels are connected to the neighbor with the
most similar color. Region boundaries are superimposed to emphasize
details.
- Comparison of the FHS with other methods. The output
differs for different algorithms. The EGB uses random
coloring scheme. JSEG algorithm superimposes region boundaries on the
original image.
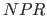 index varying algorithm parameters: (a) maximal
index varying algorithm parameters: (a) maximal 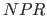 index,
(b) distribution of the maximal
index,
(b) distribution of the maximal 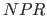 index, (c) mean
index, (c) mean 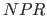 index, (d)
standard deviation of the
index, (d)
standard deviation of the 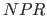 index
index
- Algorithms running time: Plots (a), (b) and (c) show running
times of evaluated algorithms vs. controlling
parameters. Plot (d) represents running time vs. image
resolution.
Damir Krstinic
2011-11-04
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES/primjeri/skoj-molo.eps}](img107.png)
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES/primjeri/kuzma1-manjo-hr08-s003.eps}](img108.png)
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES/primjeri/skoj-molo-hr08-s003.eps}](img109.png)
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES/primjeri/kuzma1-manjo-hr16-s003.eps}](img110.png)
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES/primjeri/skoj-molo-hr16-s003.eps}](img111.png)
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES/primjeri/kuzma1-manjo-hr16-s050.eps}](img112.png)
![\includegraphics[height=4.6cm]{IMAGES//primjeri/skoj-molo-hr16-s050.eps}](img113.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/253036.ppm.eps}](img114.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/MSE-08.ppm.eps}](img115.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/FHS-04.ppm.eps}](img116.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/EGB-300.ppm.eps}](img117.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/FHS-12.ppm.eps}](img118.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/JSEG.ppm.eps}](img119.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/FHS-20.ppm.eps}](img120.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.0cm]{IMAGES/subjective/253036/MS-GNM.png.eps}](img121.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/maxNPR-FHS.eps}](img122.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/maxNPR-hist-FHS.eps}](img123.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES//meanNPR-FHS.eps}](img124.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/stdev-hist-FHS.eps}](img125.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/ambis-time-FHS.eps}](img126.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/ms-time-FHS.eps}](img127.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/egb-time-FHS.eps}](img128.png)
![\includegraphics[width=7.9cm]{IMAGES/size-time-FHS.eps}](img129.png)